THE PASSIVIZATION
A sentence can be either active or passive.
In Active sentence, subject performs the action.
Ex: Keshav teaches English.
In Passive sentence, subject reveives action.
Ex: English is taught by Keshav.
Generally active sentences are more
common than passive sentences except in some text types. Some style books
advise us against the overused of passive sentences which makes the writing
depersonalized and heavy. For example, bureaucratic language i.e., the language
used by the Government officials/agencies contain excessive use of
passivization.
The Passive voice should be used only
when it is appropriate or necessary as in the following example. The
Earth was formed millions of years ago. Here by whom is unknown or
unknowable. So, the passive voice is more appropriate. The use of passive form
should be restricted to about one fourth of the time.
• The passive voice is formed then only
when there is a possibility to ask a question what? Ex: Ram
painted a wall. Ram painted what? Then answer is wall. So here we
can construct passive. Another Example:
Seetha
went to market. Here we do not construct a question with what. If we
want to construct a question that is formed by where, as Where did
Seetha go? So passive form is not constructed for such sentences.
Rules to transform from Active to
Passive:
• The active subject becomes the passive
object.
• The active object becomes the passive
subject.
• Some form of be is introduced
before the main verb which itself be changed to the past participle (v3) form.
• The preposition by is
introduced before the agent.
• The agent may be absent in some
passives but there is an implication of its presence at the level of meaning.
When do we use Passive form?
· · When we don’t know the agent (subject) When we use an indefinite or vogue pronoun or noun (Somebody, they, people, we etc. as subject in active voice.
o
Ex: My pen has been stolen. ( Somebody
has stolen my pen).
o
I was asked my name. ( They asked me
my name.)
o
English is spoken all over the world.
(People speak English all over the world.)
o
I have been invited to the party. (
Someone has invited me to the party)
o
All orders will be executed promptly.
(we will execute all orders promptly)
·
When the subject is not important/
known to everyone.
o
The rat was eaten. (by cat)
o
The building was renovated. ( when doer
of the action is not important)
o
The thief was arrested (subject is
well known, by police)
·
To shift the focus (on subject or
object) When
o
The roads were fixed quickly (by govt,
but by whom is not important here)
o
The Govt fixed the roads quickly. ( focus
is on govt, instead of action)
o
The aeroplane was invented in 20th
century. (information, here the focus is on aeroplane not on inventor)
o
Wright brothers invented the
aeroplane. (focus is on the subject, not of aeroplane)
Note: In such cases the agent ‘by’ is usually avoided. The ‘by’ phrase
can’t be avoided where the agent has some importance.
• For official rules. Ex: All taxes
must be paid before 31stMarch.
• In text books and reports. Ex: Energy
consumption was defined to include natural gas, oil and electricity used in the
residential, commercial industrial sectors.
• In news reports. Ex: Talks will be
held in Delhi next week on Telangana issue. Buses were damaged by
demonstrators.
• In deciding experiments in science and
technology. Ex: The laboratory results were examined by Dr. Johnson. Test
tube is placed in heat.
• For courtesy and modesty. Ex: Passengers
are requested to kindly refrain from smoking. You are cordially invited.
• In describing process. Ex: Two
glasses of rice is taken in a dish. The dishis placed on the fire.
• In newspaper headlines: Ex: Two
people were killed in a road mishap.
Exemptions
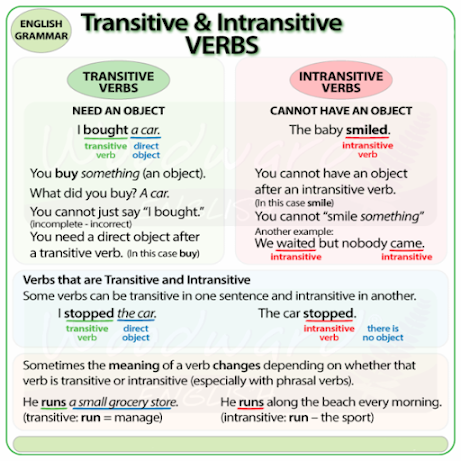
• In-transitive verbs (which have no
objects) cannot be used in the passive forms because there is nothing to become
the subject of a passive sentence. Ex: die, arrive, appear, become, come,
fall, go, have, live, travel, work.
Do + something ----> Transitive ----> He stopped the car; He writes stories.
( Do+something is possible)
Do ----> Intranstive ----> Raju came; Ravi is sleeping.
(Do+something is not possible)
• Active sentences which do not form a
question with what.
• Please note that there are only 8
tense forms in Passive Voice
Construction Rules:
Rule 1: For
a verb in Simple Present/Present Indefinite tense use is, am or are
before the 3rd form of the verb in passive voice. Ex:
|
Active voice |
Passive
voice |
|
1.
Sangitha Sings a song |
A song is sung
by Sangitha |
|
1.
He helps me |
I am helped by him. |
|
2.
Children make a noise |
A noise is made by Children. |
|
3.
Does he take tea? |
Is tea taken by him? |
|
4.
Do you play any game? |
Is any game played by you? |
Rule 2: For a verb in Simple Past/Past Indefinite tense use was or were before the third form of the verb in passive voice. Ex:
|
Active voice |
Passive
voice |
|
1.
Sangitha sang a song |
A song was sung
by Sangitha |
|
2.
He helped me. |
I was helped by him. |
|
3.
Children made a noise |
A noise was made by Children. |
|
4.
Did he take tea? |
Was tea taken by him? |
|
5.
Did you play any game? |
Was any game played by you? |
Rule 3: For a
verb in Simple Future/Future Indefinite tense use be-form before the third form of the verb in passive
voice. Ex:
|
Active voice |
Passive
voice |
|
1.
Sangitha will sing a song |
A song will be sung
by Sangitha |
|
2.
He will help me. |
I will/shall be helped by him. |
|
3.
Children will make a noise |
A noise will be made by Children. |
|
4.
Will he take tea? |
Will tea be taken by him? |
|
5.
Will you play any game? |
Will any game be played by you? |
Rule 4: For a verb in Present Continuous tense use is, am or are before the third form of the verb in passive voice. For a verb in Past Continuous tense use was or were in before the third form of the verb in the Passive Voice. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
|
|
|
I am writing a
letter |
A letter is being written by me |
|
The boys were playing cricket |
Cricket was being played by the boys |
|
Is he helping
you? |
Are you being
helped by him? |
|
He was giving a
pen |
A pen was being
given by him. |
|
Was he taking tea? |
Was tea being taken by him? |
Rule 5: For a verb in the Present Perfect or the Past Perfect Tense, use been before the third form of the verb. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
She has taken
my book. |
My book has
been taken by her. |
|
I have done my
duty. |
My duty has
been done by me |
|
Have you heard
the news? |
Has the news
been heard by you? |
|
I had not seen
a lion before. |
A lion had not been seen by me before |
|
He will have finished the work. |
The work will have been finished by him |
Rule 6: For sentences with the helping verb can, may, must, should, would, could, might etc use ‘be’ before the third form of the main verb. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
|
|
|
I can do it. |
It can be done
by me. |
|
We may win the
match |
The match can
be won by us |
|
You must keep
your promise? |
Your promise must be kept by you |
|
You should read
this book. |
This book
should be read by you. |
|
You ought to help him. |
He ought to be helped by you. |
Rule 7:For a verb in an Imperative sentence use ‘let’ before the 3rd form of the main verb. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
|
|
|
Open the door. |
Let the door be
opened. |
|
Respect your
teacher |
Let your
teachers be respected |
|
Do not waste
time |
Let time not be
wasted. |
|
Never tell a
lie |
Let a lie be
never told |
|
Take left turn. |
Let the left turn be taken. |
Rule 8:For a verb with two objects, make any object as the subject. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
|
|
|
She gave me a
book. |
A book was
given to me by her. (or) I was
given a book by her. |
|
We offered him
tea. |
Tea was offered
by us to him. (or) He was
offered tea by us. |
Rule 9: For a verb with a preposition coming
in it, regard the preposition as a part of the verb.Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
Sudha spoke to
me. |
I was spoken to
by Sudha. |
|
They are laughing at him. |
He is being laughed at by them. |
Rule 10: Interrogatives takes the following
structure. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
Do you eat
meat? |
Is meat eaten
by you? |
|
Did they take
photos? |
Were photos
taken by him? |
|
Can you speak
English? |
Can English be
spoken by you? |
|
Why do you
waste money? |
Why is money
wasted by you? |
|
When will he
begin the work? |
When will the work be begun by him? |
|
Who wrote the
exam? |
By whom was the
exam written? |
|
Who can speak
English? |
By whom can
English be spoken? |
|
Whom do you meet? |
Who is met by you? |
|
Whom did you
like? |
Who was liked
by you? |
|
What do you
want? |
What is wanted
by you? |
|
What have you
eaten? |
What has been
eaten by you? |
|
Has a dog
bitten you? |
Have you been
bitten by a dog? |
|
Get out. |
You are ordered to get out |
Rule 11: Observe the following changes in
place of by in passive construction. Ex:
|
ACTIVE VOICE |
PASSIVE VOICE |
|
|
|
|
….know/marry |
known/married to |
|
…please/satisfy/
vexed / delight/ anger |
pleased/satisfied/vexed/
delighted/ anger with |
|
…surprise |
surprised at |




0 comments:
Post a Comment